Learn how to collect and display data using loops, actions, and variables.
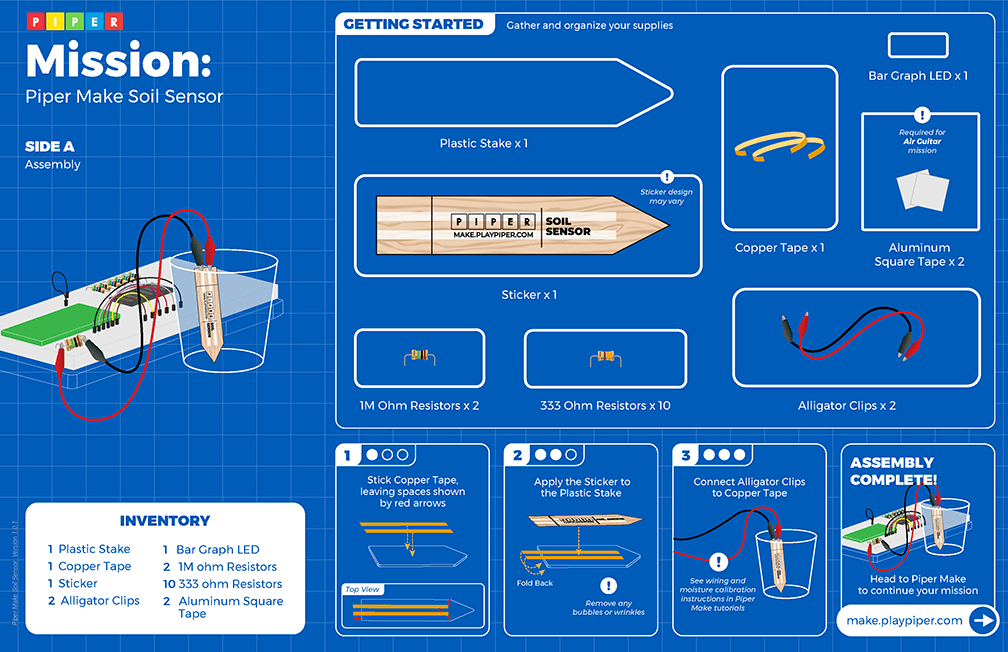
Piperbot and Pip are excited to find sustainable farming operations on Mars! Let's build a Soil Sensor to measure how much water reaches the plants.
View student interface at make.playpiper.com Computer with USB port and Chrome or Edge browser
Computer with USB port and Chrome or Edge browser
 Piper Make Base Station or Starter Kit
Piper Make Base Station or Starter Kit
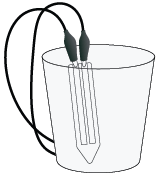 Soil Sensor
Soil Sensor
The following sections will contain step by step instructions for ELA, ELD and Math extensions directly related to this mission. Adjust the directions to fit your ELA, ELD and Math standards.
ELA Extension: Write a StoryAsk students to write a narrative story from the point of view of the plant.
Math Extension:
Ask students to use the reading in the Console to determine the average.
 Natural Sciences Manager: Salary $144,440/yr
Natural Sciences Manager: Salary $144,440/yr
 Agricultural Engineer: Salary $83,260/yr
Agricultural Engineer: Salary $83,260/yr
 Environmental Engineer: Salary $96,530/yr
Environmental Engineer: Salary $96,530/yr
 Soil and Plant Scientist: Salary $65,730/yr
Soil and Plant Scientist: Salary $65,730/yr
Fossil Fuels Sources of energy made from prehistoric plants and animals (coal, oil, natural gas). (CE)
Renewable Energy Energy sources from natural resources that can be more easily replenished (solar, water, nuclear). (CE)
Capacitance An object's ability to hold an electric charge.
Pollution Anything that dirties the Earth, such as litter, smoke from cars and factories, or water contamination. (CE)
