Let’s go head to head! With V1 of Beam Break, set up two side by side tracks and use the two IR beams to measure which car breaks the beam first. With V2, use the Beam Break mission and compare it to your neighbor’s time. Discuss how you would compare the two times in code to determine a winner.
View student interface at make.playpiper.com Computer with USB port and Chrome or Edge browser
Computer with USB port and Chrome or Edge browser
 Piper Make Base Station or Starter Kit
Piper Make Base Station or Starter Kit
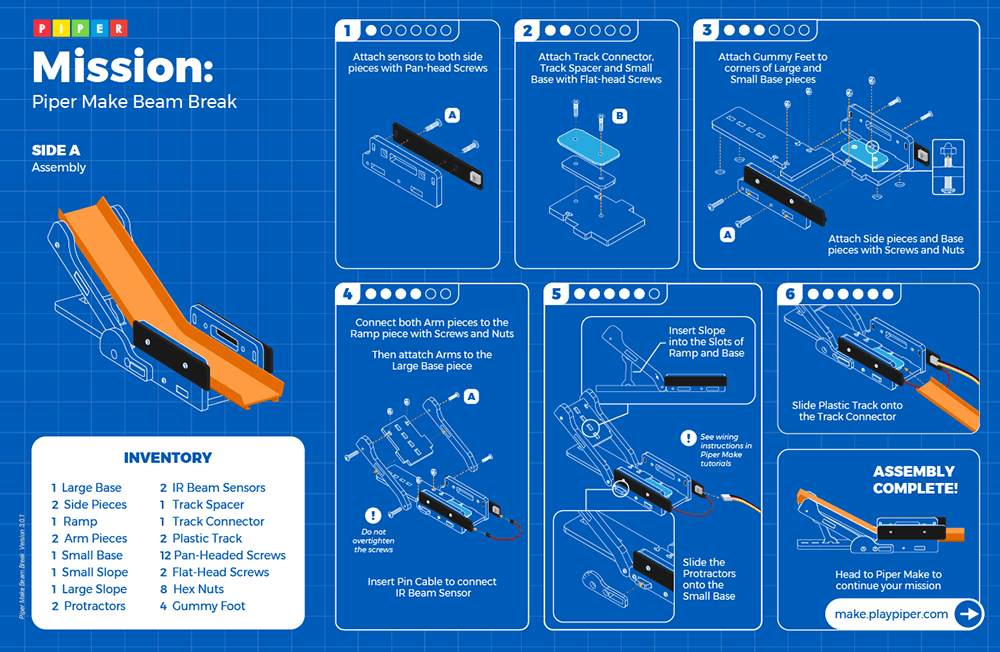
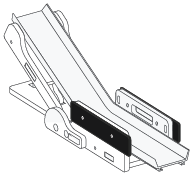 Beam Break
Beam Break
 Urban and Regional Planner: Salary $79,540/yr
Urban and Regional Planner: Salary $79,540/yr
 Sports Official: Salary $36,010/yr
Sports Official: Salary $36,010/yr
 Physicist: Salary $142,850/yr
Physicist: Salary $142,850/yr
 Avionics Technicians: Salary $75,450/yr
Avionics Technicians: Salary $75,450/yr
What are Pull-Up and Pull-Down Resistors?
Velocity Another word for speed or the rate of change in an object’s position. (MB / BB)
Acceleration Measurement of the change in velocity or how much an object speeds up over time (MB / BB)
Kinetic Energy Energy an object has due to its motion. It can be converted from potential energy. (MB / BB)
Potential Energy Energy stored by an object due to its state or position; can be converted to kinetic energy. (MB / BB)
Force A push or pull on an object, measured in pounds (imperial) or Newtons (metric). (MB / BB)
Momentum Measurement of mass in motion equal to the mass times the velocity of an object. (MB / BB)
