Computing Systems: Devices
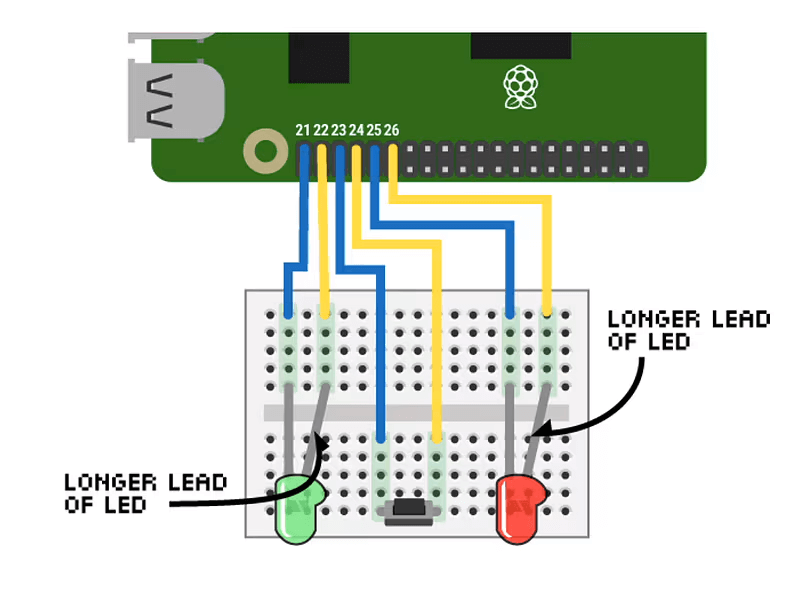
 Piper Computer Kit
Piper Computer Kit
Encourage students to complete the Frog Frenzy project.
During this time, roam around the room, asking the essential questions* of this lesson: Data Scientist: Salary $103,500/yr
Data Scientist: Salary $103,500/yr
 Graphic Designer: Salary $58,910/yr
Graphic Designer: Salary $58,910/yr
 Web Developer: Salary $84,960/yr
Web Developer: Salary $84,960/yr
 Video Game Designer: Salary $83,240/yr
Video Game Designer: Salary $83,240/yr
Program An algorithmic set of instructions a computer processes to achieve a particular objective. Humans use computational thinking to create programs.
Python A text-based programming language used in many career fields like web development, artificial intelligence, data analysis, and game development.
Hardware Hardware refers to the physical parts of a computer or electronic device that you can touch and see .
We are excited to be aligned with the following standards.

| Concepts | Standards |
|
Computing Systems: Devices |
CA 3-5.CS.1 Describe how computing devices connect to other components to form a system. (P7.2) |
|
Computing Systems: Hardware & Software |
CA 3-5.CS.2 Demonstrate how computer hardware and software work together as a system to accomplish tasks. (P4.4) 6-8.CS.2 Design a project that combines hardware and software components to collect and exchange data. (P5.1) |
|
Computing Systems: Troubleshooting |
3-5.CS.3 Determine potential solutions to solve simple hardware and software problems using common troubleshooting strategies. (P6.2) 6-8.CS.3 Systematically apply troubleshooting strategies to identify and resolve hardware and software problems in computing systems. (P6.2 |
|
Algorithms & Programming: Algorithms Variables Control Modularity Program Development |
3-5.AP.11 Create programs that use variables to store and modify data. (P5.2) 3-5.AP.12 Create programs that include events, loops, and conditionals. 3-5.AP.13 Decompose problems into smaller, manageable tasks which may themselves be decomposed. (P3.2) 3-5.AP.14 Create programs by incorporating smaller portions of existing programs, to develop something new or add more advanced features. (P4.2, P5.3) 3-5.AP.17 Test and debug a program or algorithm to ensure it accomplishes the intended task. (P6.2) 3-5.AP.18 Perform different roles when collaborating with peers during the design, implementation, and review stages of program development. 6-8.AP.10 Use flowcharts and/or pseudocode to design and illustrate algorithms that solve complex problems. (P4.1, P4.4) 6-8.AP.11 Create clearly named variables that store data, and perform operations on their contents. (P5.1, P5.2) 6-8.AP.13 Decompose problems and subproblems into parts to facilitate the design, implementation, and review of programs. (P3.2) 6-8.AP.14 Create procedures with parameters to organize code and make it easier to reuse. (P4.1, P4.3) 6-8.AP.15 Seek and incorporate feedback from team members and users to refine a solution that meets user needs. (P1.1, P2.3) 6-8.AP.17 Systematically test and refine programs using a range of test cases. (P6.1) 6-8.AP.19 Document programs in order to make them easier to use, read, test, and debug. (P7.2) |
|
Impacts of Computing and Social Interactions |
3-5.IC.22 Seek and explain the impact of diverse perspectives for the purpose of improving computational artifacts. (P1.1) 6-8.IC.22 Collaborate with many contributors when creating a computational artifact. (P2.4, P5.2) |
|
Practices |
P1. Fostering an Inclusive Computing Culture P2. Collaborating Around Computing P4. Developing and Using Abstractions P5. Creating Computational Artifacts P6. Testing and Refining Computational Artifacts |

| Concept | Standard |
|
Make observations to provide evidence that energy can be transferred from place to place by sound, light, heat, and electric currents. |
|
|
Apply scientific ideas to design, test, and refine a device that converts energy from one form to another. |
(4-PS3-4) |
|
Generate and compare multiple solutions that use patterns to transfer information. |
(4-PS4-3) |
|
Generate and compare multiple possible solutions to a problem based on how well each is likely to meet the criteria and constraints of the problem (Performance Expectation). |
|
|
Plan and carry out fair tests in which variables are controlled and failure points are considered to identify aspects of a model or prototype that can be improved. (P.E.3.4.7) |
|
|
Integrate qualitative scientific and technical information to support the claim that digitized signals are a more reliable way to encode and transmit information than analog signals. |
(MS-PS4-3) |
|
Digitized signals (sent as wave pulses) are a more reliable way to encode and transmit information (inputs and outputs). |
(MS-PS4-3) |
|
Evaluate competing design solutions using a systematic process to determine how well they meet the criteria and constraints of the problem. |
|
|
Optimizing the Design Solution Different solutions need to be tested in order to determine which of them best solves the problem, given the criteria and the constraints. |