Computing Systems: Devices
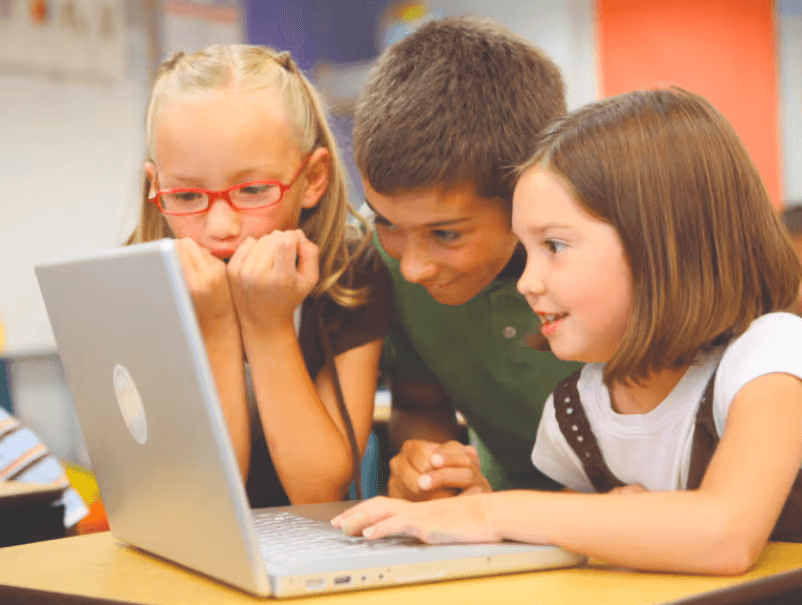

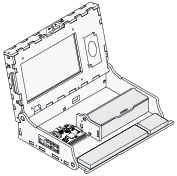 Piper Computer Kit
Piper Computer Kit
During this time, students can compare how they use computers in their lives. Use Slide 4.
Jigsaw: Students are split into groups with one member assigned to each computer. Working individually, each student learns about his or her computer and presents it to their group. Next, students gather into groups divided by type of computer. Each member presents again to the topic group. In same-topic groups, students reconcile points of view and synthesize information. They create a final report. Finally, the original groups reconvene and listen to presentations from each member. The final presentations provide all group members with an understanding of their own type of computer, as well as the findings that have emerged from topic-specific group discussion.
There are organizations that provide computers for communities around the world. What do you think they have to consider when selecting computers?
Example: There is a community in the mountains of Peru that have to use electricity generated from a small personal windmill What kind of computer would this community need?
 Economist: Salary $115,730/yr
Economist: Salary $115,730/yr
 Pilot: Salary $219,140/yr
Pilot: Salary $219,140/yr
 Healthcare Professional: Salary $224,640/yr
Healthcare Professional: Salary $224,640/yr
 Database Architect: Salary $134,700/yr
Database Architect: Salary $134,700/yr
 DOWNLOAD
DOWNLOAD
GPIO (General Purpose Input Output) Pins Pins on a microcomputer or microcontroller that can be programmed to send or receive electrical signals. They can be connected to almost anything (such as buttons and LEDs).
Raspberry Pi A small, low-cost microcomputer. Together with the Raspberry Pi OS, a special operating system, it can do many things that a full-sized computer can do.
Jumper Wires Wires used to connect from the GPIO to the breadboard. Jumper wires can have different kinds of connections on their ends, such as plugs, sockets, or alligator clips.
We are excited to be aligned with the following standards.

| Concepts | Standards |
|
Computing Systems: Devices |
CA 3-5.CS.1 Describe how computing devices connect to other components to form a system. (P7.2) |
|
Computing Systems: Hardware & Software |
CA 3-5.CS.2 Demonstrate how computer hardware and software work together as a system to accomplish tasks. (P4.4) 6-8.CS.2 Design a project that combines hardware and software components to collect and exchange data. (P5.1) |
|
Computing Systems: Troubleshooting |
3-5.CS.3 Determine potential solutions to solve simple hardware and software problems using common troubleshooting strategies. (P6.2) 6-8.CS.3 Systematically apply troubleshooting strategies to identify and resolve hardware and software problems in computing systems. (P6.2 |
|
Algorithms & Programming: Program Development |
3-5.AP.18 Perform different roles when collaborating with peers during the design, implementation, and review stages of program development. 6-8.AP.15 Seek and incorporate feedback from team members and users to refine a solution that meets user needs. (P1.1, P2.3) 6-8.AP.18 Distribute tasks and maintain a project timeline when collaboratively developing computational artifacts. (P2.2, P5.1) 6-8.AP.19 Document programs in order to make them easier to use, read, test, and debug. (P7.2) |
|
Practices |
P1. Fostering an Inclusive Computing Culture P2. Collaborating Around Computing P4. Developing and Using Abstractions P5. Creating Computational Artifacts P6. Testing and Refining Computational Artifacts |

| Concept | Standard |
|
Apply scientific ideas to design, test, and refine a device that converts energy from one form to another. |
(4-PS3-4) |
|
Generate and compare multiple solutions that use patterns to transfer information. |
(4-PS4-3) |
|
Waves and their Applications in Technologies for Information Transfer Connection to the Nature of Science: Science knowledge is based upon logical and conceptual connections between evidence and explanations. |
(MS-PS4-1) |
|
Generate and compare multiple possible solutions to a problem based on how well each is likely to meet the criteria and constraints of the problem (Performance Expectation).; |
|
|
Plan and carry out fair tests in which variables are controlled and failure points are considered to identify aspects of a model or prototype that can be improved. (P.E.3.4.7) |
|
|
Optimizing the Design Solution; Different solutions need to be tested in order to determine which of them best solves the problem, given the criteria and the constraints. |