Computing Systems: Devices
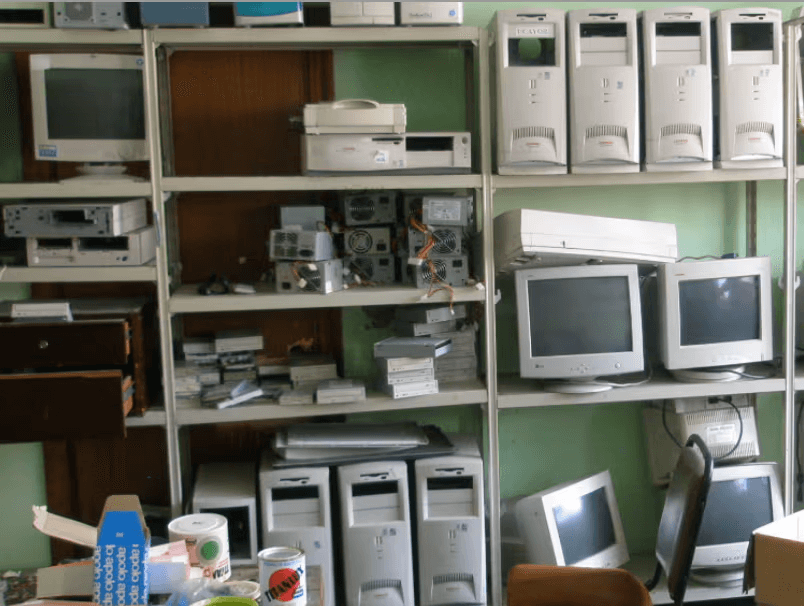

 Piper Computer Kit
Piper Computer Kit
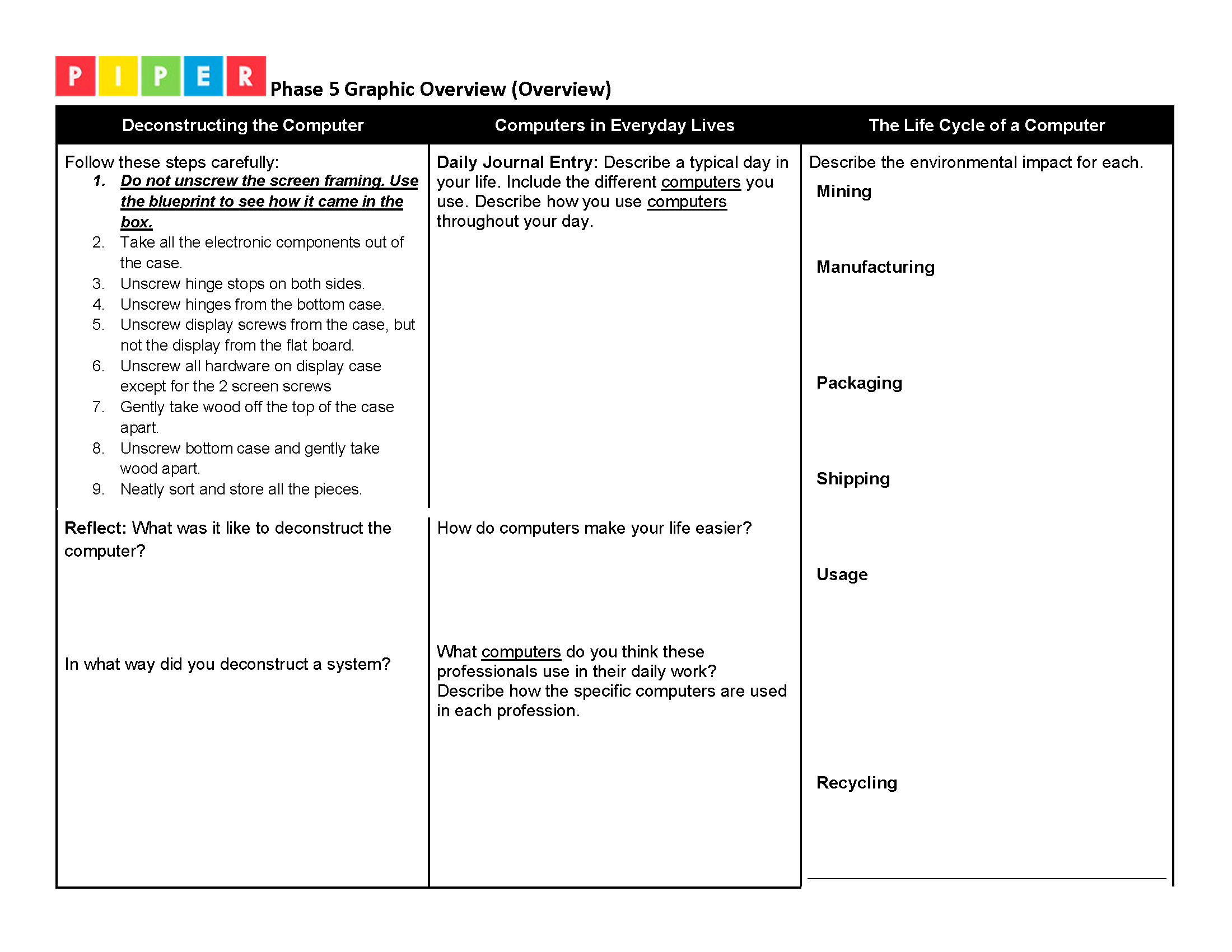
Present this essential question to students: How does using a computer affect the environment?
Have students work in groups to answer the following questions using their Piper Computer Kits:How would you describe the impact that one computer has on the environment?
Use slides 4-10 to discuss the life cycle of a computer.
Cost is also a consideration when making a computer. Research the cost of creating one computer.
Ask the students the following: Economist: Salary $115,730/yr
Economist: Salary $115,730/yr
 Pilot: Salary $219,140/yr
Pilot: Salary $219,140/yr
 Healthcare Professional: Salary $224,640/yr
Healthcare Professional: Salary $224,640/yr
 Database Architect: Salary $134,700/yr
Database Architect: Salary $134,700/yr
 DOWNLOAD
DOWNLOAD
Recycling The process of taking used materials or products and turning them into new ones instead of throwing them away.
Manufacturing The process of making products in large quantities using machines, tools, and workers. It’s how products are built and prepared for people to use.
Environment The natural world around us, including the air, water, land, plants, and animals.
We are excited to be aligned with the following standards.

| Concepts | Standards |
|
Computing Systems: Devices |
CA 3-5.CS.1 Describe how computing devices connect to other components to form a system. (P7.2) |
|
Computing Systems: Hardware & Software |
CA 3-5.CS.2 Demonstrate how computer hardware and software work together as a system to accomplish tasks. (P4.4) 6-8.CS.2 Design a project that combines hardware and software components to collect and exchange data. (P5.1) |
|
Computing Systems: Troubleshooting |
3-5.CS.3 Determine potential solutions to solve simple hardware and software problems using common troubleshooting strategies. (P6.2) 6-8.CS.3 Systematically apply troubleshooting strategies to identify and resolve hardware and software problems in computing systems. (P6.2 |
|
Algorithms & Programming: Program Development |
3-5.AP.18 Perform different roles when collaborating with peers during the design, implementation, and review stages of program development. 6-8.AP.15 Seek and incorporate feedback from team members and users to refine a solution that meets user needs. (P1.1, P2.3) 6-8.AP.18 Distribute tasks and maintain a project timeline when collaboratively developing computational artifacts. (P2.2, P5.1) 6-8.AP.19 Document programs in order to make them easier to use, read, test, and debug. (P7.2) |
|
Practices |
P1. Fostering an Inclusive Computing Culture P2. Collaborating Around Computing P4. Developing and Using Abstractions P5. Creating Computational Artifacts P6. Testing and Refining Computational Artifacts |

| Concept | Standard |
|
Apply scientific ideas to design, test, and refine a device that converts energy from one form to another. |
(4-PS3-4) |
|
Generate and compare multiple solutions that use patterns to transfer information. |
(4-PS4-3) |
|
Waves and their Applications in Technologies for Information Transfer Connection to the Nature of Science: Science knowledge is based upon logical and conceptual connections between evidence and explanations. |
(MS-PS4-1) |
|
Generate and compare multiple possible solutions to a problem based on how well each is likely to meet the criteria and constraints of the problem (Performance Expectation).; |
|
|
Plan and carry out fair tests in which variables are controlled and failure points are considered to identify aspects of a model or prototype that can be improved. (P.E.3.4.7) |
|
|
Optimizing the Design Solution; Different solutions need to be tested in order to determine which of them best solves the problem, given the criteria and the constraints. |