Develop a model to describe that matter is made of particles too small to be seen.
 Piper Computer Kit
Piper Computer Kit
 Sensor Explorer Kit
Sensor Explorer Kit
Use slides 1-4 in the Lesson 3 Slide Deck to help students investigate current sensor alarms available on Amazon.
Provide students with samples of sensor alarms or have them look for them in a reliable search engine. Have them consider why and when this type of alarm would be useful. Students can think-pair-share or have an open class discussion.
Have students revisit the StoryMode level but now focusing on the questions below.
Have students complete the PiperCode project Security Zone. During this PiperCode Project, students will code their own sensor alarm using the Distance Sensor and the Piper Computer Kit. Before they begin, show students slides 3 and 4 in the Lesson 3 Slide Deck to remind students about wiring troubleshooting.
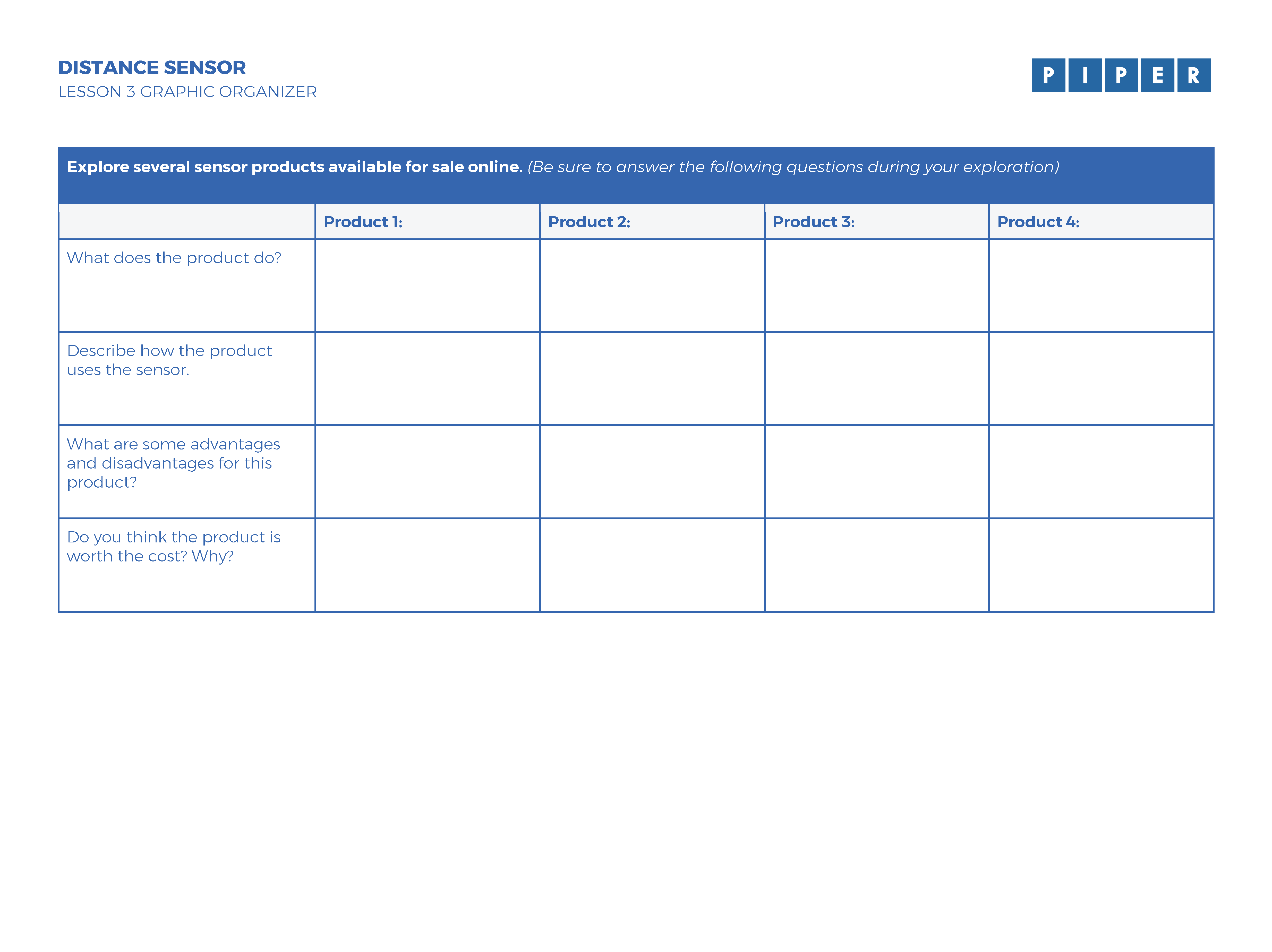
Have students record their responses to the Discussion Questions found in the tutorial as they complete the project on this graphic organizer.
Have students use the graphs they created on their graphic organizers for the explanation.
Use slide 5 to review the different graphs created by each group. Through this explanation, students should touch on their responses to the discussion questions.Students learned of echolocation in Lesson 2. Lesson 3 is the technological application of this concept.
Sonar is one application that helps submarines “see” when below the water. Students can learn more about this by reading this article. Have them write a reflection in their journals.At the end of this lesson, have student take the Assessment.
 Security/Fire System Installers: Salary $50,130/yr
Security/Fire System Installers: Salary $50,130/yr
 Civil Engineer: Salary $88,050/yr
Civil Engineer: Salary $88,050/yr
 Construction Manager: Salary $101,480/yr
Construction Manager: Salary $101,480/yr
 Avionics Technicians: Salary $75,450/yr
Avionics Technicians: Salary $75,450/yr
 DOWNLOAD
DOWNLOAD
Pattern Something that repeats in a predictable way. In color sensors, a pattern is something like stripes or spots that the sensor looks for to recognize and understand what it's seeing. It helps the sensor tell different colors or shapes apart by noticing these repeating designs.
Transmittance How much light passes through a material. In color sensors, it measures how much light goes through an object or material without being absorbed or reflected.
Alarm A device that warns or signals, as by a bell, buzzer or whistle .
We are excited to be aligned with the following standards.

| Concept | Standard |
|
Develop a model to describe that matter is made of particles too small to be seen. |
3-5-PS1-1 |
|
Make observations and/or measurements of an object’s motion to provide evidence that a pattern can be used to predict future motion. |
3-PS2-2 |
|
Develop a model of waves to describe patterns in terms of amplitude and wavelength and that waves can cause objects to move. |
4-PS4-1 |
|
Develop a model to describe that light reflecting from objects and entering the eye allows objects to be seen. |
4-PS4-2 |
|
Generate and compare multiple solutions that use patterns to transfer information. |
4-PS4-3 |
|
Use a model to describe that animals receive different types of information through their senses, process the information in their brain, and respond to the information in different ways. |
4-LS1-2 |
|
Develop a model to describe the cycling of matter and flow of energy among living and nonliving parts of an ecosystem. |
MS-LS2-3 |
|
Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance when thermal energy is added or removed. |
MS-PS1-4 |
|
Plan an investigation to determine the relationships among the energy transferred, the type of matter, the mass, and the change in the average kinetic energy of the particles as measured by the temperature of the sample. |
MS-PS3-4 |
|
Construct, use, and present arguments to support the claim that when the kinetic energy of an object changes, energy is transferred to or from the object. |
MS-PS3-5 |
|
Develop a model to describe that waves are reflected, absorbed, or transmitted through various materials. |
MS-PS4-2 |
|
Develop a model to describe the cycling of water through Earth's systems driven by energy from the sun and the force of gravity. |
MS-ESS2-4 |
|
Ask questions to clarify evidence of the factors that have caused the rise in global temperatures over the past century. |
MS-ESS3-5 |
|
Obtain and combine information to describe climates in different regions of the world. |
3-ESS2-2 |