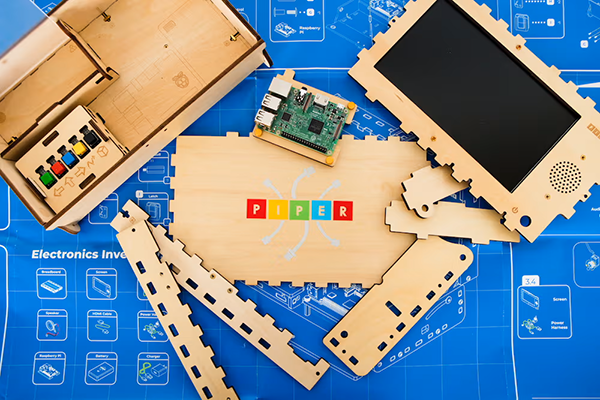
 Piper Computer Kit
Piper Computer Kit
Show students the Ted Talk on the invention of the washing machine. Ask: “How did the invention of this technology change the speaker’s life? What technology has had this kind of impact on your life? What technology do you use the most at school?”
The goal is to get students considering the importance of computers in their lives.
Guiding questions that can be displayed or handed out: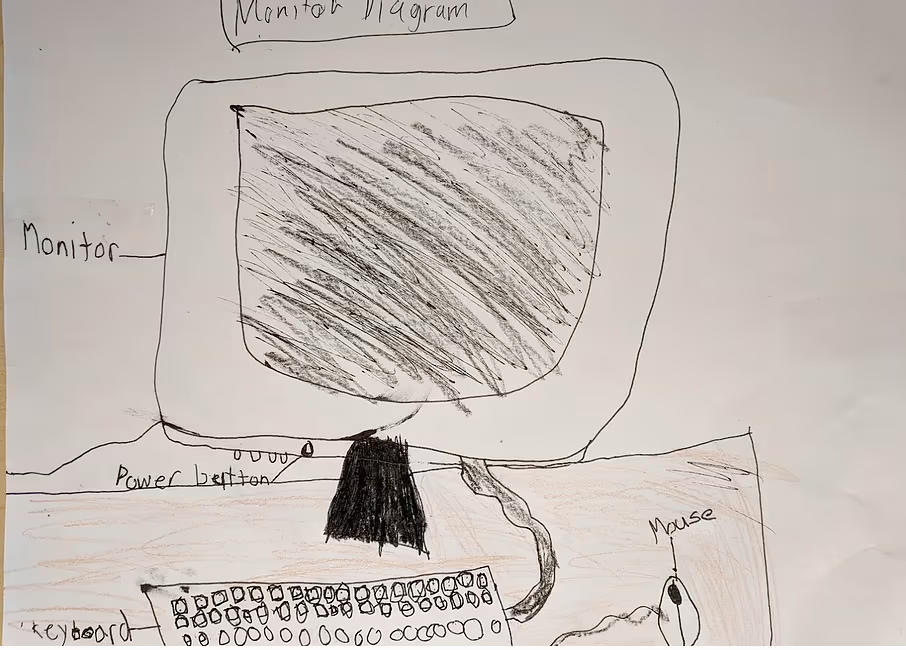
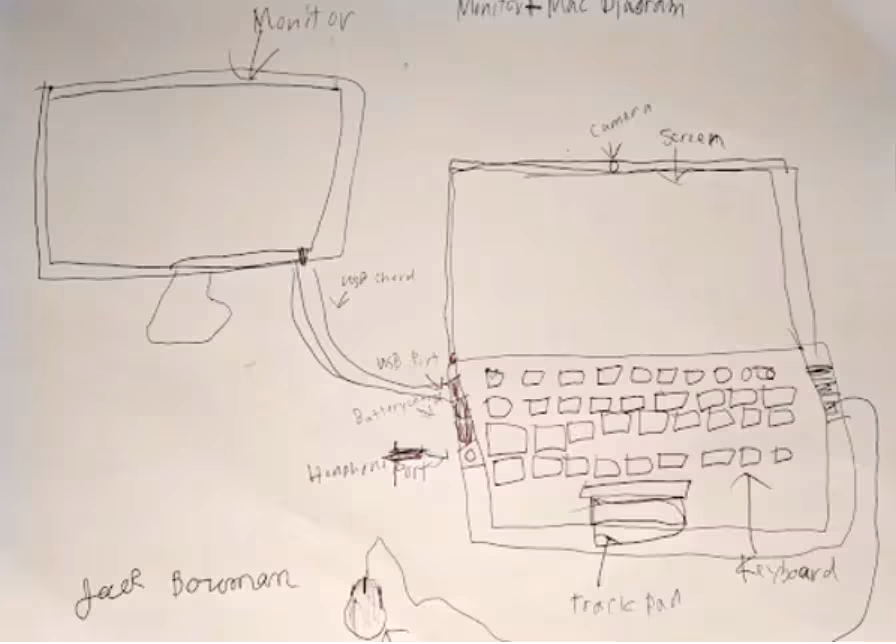
After students draw, tell them to Think, Pair & Share. Think-Pair-Share (TPS) is a versatile cooperative learning activity suitable for any subject and class size. Instructors pose a question, students first THINK independently, then discuss their responses with a nearby peer (PAIR).
Introduce the Piper experience to the students: “When an engineer wants to know how something works, they tend to start inside. You will begin by building a working computer to learn what is inside and how it works. Then, we will learn to code through games and projects on that computer.”
“You’ll be building the computer from parts in a box, including constructing the case, connecting the components, and working as a team to be an engineer and solve problems that you encounter. We were given one very important tool in the box (hold up example): this engineering blueprint. How will you use the blueprint to learn how a computer works?”
Use Lesson 1.1 Slides to debrief with the teams.
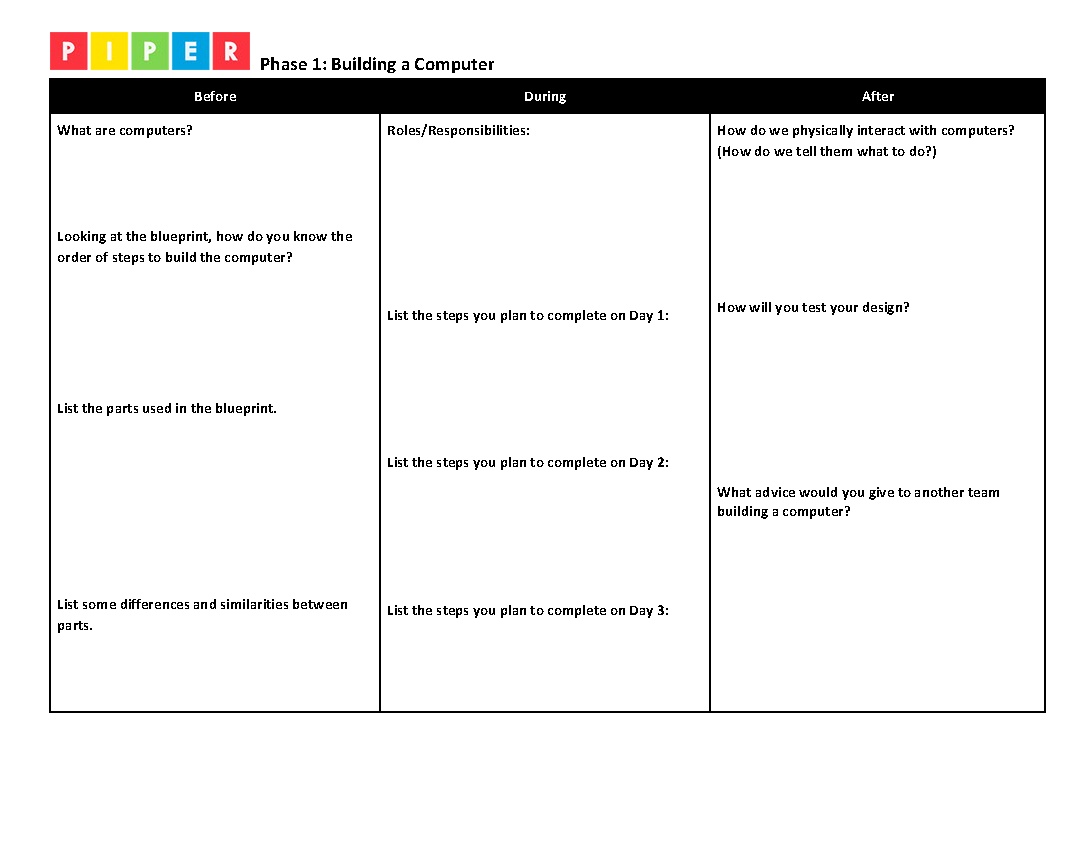
This will help guide students as they complete the first column of their graphic organizer.
Students will be answering the following questions on their graphic organizers:Students share their roles and responsibilities for each member of their team. (Middle column of visual organizer.)
At the end of this lesson, have student take the Assessment.
 Project Manager: Salary $104,920/yr
Project Manager: Salary $104,920/yr
 Construction Manager: Salary $101,480/yr
Construction Manager: Salary $101,480/yr
 Architect: Salary $93,310/yr
Architect: Salary $93,310/yr
 Computer Hardware Engineer: Salary $132,360/yr
Computer Hardware Engineer: Salary $132,360/yr
 DOWNLOAD
DOWNLOAD
Blueprint A detailed plan or a map for building something.
Inventory A list of all the things you have in one place.
Mouse A small device that you move with your hand to control the arrow or pointer on a computer screen.
Beginning with phase 1, all phases will align with standards that apply to all the lessons in the phase. For this phase the CA 2019 K-12 Computer Science Content Standards, 2017 Computer Science Teachers Association (CSTA) K-12 Computer Science Standards (csteachers.org/standards) and K–12 Computer Science Framework (k12cs.org) informed the development and alignment of the lessons that follow. Use them with daily or weekly agendas and planning. Phase 1 is where the learners first build a Piper kit.
We are excited to be aligned with the following standards.

| Concepts | Standards |
|
Computing Systems: Devices, Troubleshooting |
3-5.CS.1 Describe how computing devices connect to other components to form a system. (P7.2) 3-5.CS.3 Determine potential solutions to solve simple hardware and software problems using common troubleshooting strategies. (P6.2) 6-8.CS.2 Design a project that combines hardware and software components to collect and exchange data. (P5.1)
6-8.CS.3 Systematically apply troubleshooting strategies to identify and resolve hardware and software problems in computing systems. (P6.2) |
|
Algorithms & Programming |
3-5.AP.13 Decompose problems into smaller, manageable tasks which may themselves be decomposed. (P3.2) 3-5.AP.18 Perform different roles when collaborating with peers during the design, implementation, and review stages of program development (ie. following the Piper Blueprint) 6-8.AP.13 Decompose problems and subproblems into parts to facilitate the design, implementation, and review of programs. (P3.2) 6-8.AP.18 Distribute tasks and maintain a project timeline when collaboratively developing computational artifacts. (P2.2, P5.1) |
|
Impacts of Computing |
CA CS 3-5.IC.20 Discuss computing technologies that have changed the world, and express how those technologies influence, and are influenced by, cultural practices. 6-8.IC.21 Discuss issues of bias and accessibility in the design of existing technologies. (P1.2) |
|
Practices |
P1. Fostering an Inclusive Computing Culture P2. Collaborating Around Computing P4. Developing and Using Abstractions P5. Creating Computational Artifacts P6. Testing and Refining Computational Artifacts |

| Concept | Standard |
|
Generate and compare multiple solutions that use patterns to transfer information. |
|
|
Generate and compare multiple possible solutions to a problem based on how well each is likely to meet the criteria and constraints of the problem (Performance Expectation). |
|
|
Plan and carry out fair tests in which variables are controlled and failure points are considered to identify aspects of a model or prototype that can be improved. (P.E.3.4.7) |
3–5-ETS1-3 |
|
Evaluate competing design solutions using a systematic process to determine how well they meet the criteria and constraints of the problem. |
MS-ETS1-2 |