Learn how to play the Ultrasonic Range Finder as an instrument.
Piperbot and Pip need help soothing Baby Zomar to sleep. Play your Ultrasonic Range Finder as an instrument to help. Ask students: “How does your instrument know when and what sound to play? How does an electric keyboard know how to make a sound?”
View student interface at make.playpiper.com Computer with USB port and Chrome or Edge browser
Computer with USB port and Chrome or Edge browser
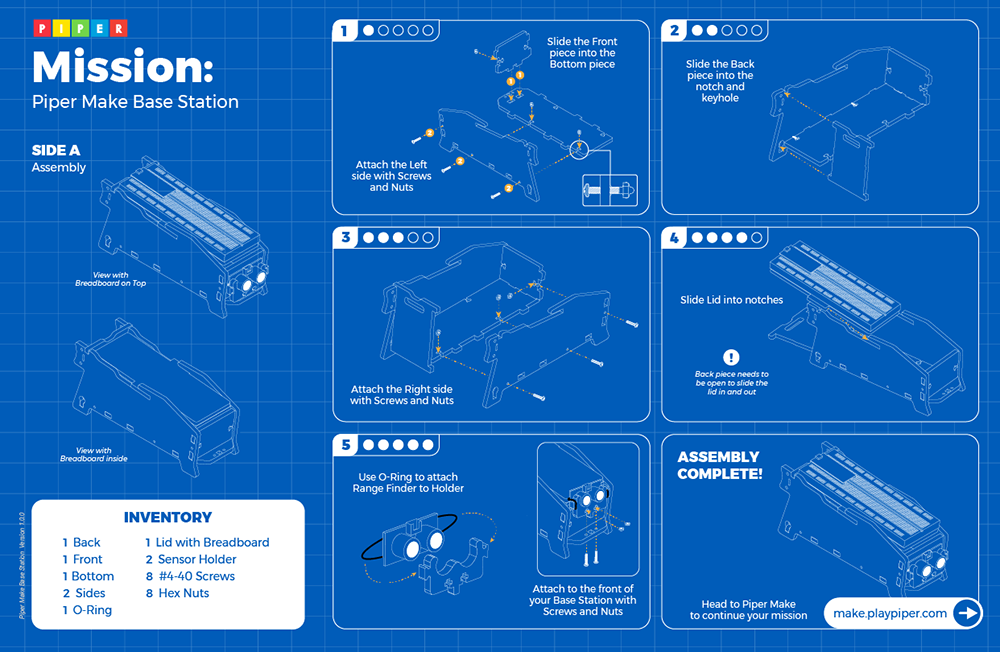
 Piper Make Base Station or Starter Kit
Piper Make Base Station or Starter Kit
 Ultrasonic Range Finder
Ultrasonic Range Finder
 Robotics Engineer: Salary $104,600/yr
Robotics Engineer: Salary $104,600/yr
 Automotive Engineer: Salary $95,300/yr
Automotive Engineer: Salary $95,300/yr
 Civil Engineer: Salary $88,050/yr
Civil Engineer: Salary $88,050/yr
 Electro-Mechanical and Mechtronics Technicians: Salary $60,570/yr
Electro-Mechanical and Mechtronics Technicians: Salary $60,570/yr
Robot A device that can execute a task independently of direct human control or activity.
Feedback Sensors Instruments that robots can use to make adjustments based on their readings.
Servo Motor Self-contained electric devices that precisely rotate or push machine parts.
Autonomous Vehicle A vehicle that can operate without direct human control, usually through a built-in autopilot system.
Bionics When we use biological systems (e.g., dogs, humans) to develop and design new robots.
