Learn about Machine Learning (AI), a subset of AI focusing on machines and very specific tasks.
Now that Piperbot and Pip have PAL up and running, they are ready to explore. Surprisingly, they've discovered that the ship's controls are damaged and can't be used on the flight deck. PAL, however, has a new idea and suggests that using a camera as a sensor, he could steer the ship based on the movements of Piperbot's head so that they could get going using the principles of Machine Learning.
View student interface at make.playpiper.com Computer with USB port and Chrome or Edge browser
Computer with USB port and Chrome or Edge browser
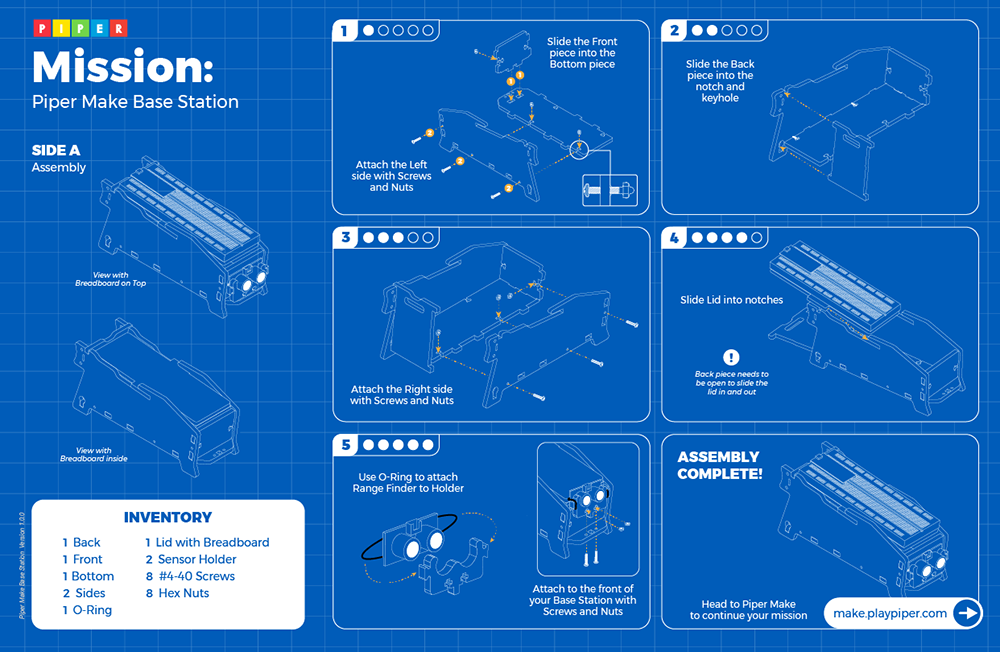
 Piper Make Base Station or Starter Kit
Piper Make Base Station or Starter Kit
The following sections will contain step by step instructions for ELA and ELD extensions directly related to this Mission. Adjust the directions to fit your ELA and ELD standards.
ELA Extension: Recognizing Piperbot Display the three character images below (Piperbot, Pip, and a creeper from Minecraft).
Ask students to share how they recognize the difference between the characters. They may say, “I’ve seen them before” or “It looks like a mouse.”
Discuss how artificial intelligence would recognize the difference between the characters - it would learn from seeing multiple images of the same character, and look for patterns. Ask students what are the patterns that tell us whether it is a robot, mouse, or creeper? Students should be able to describe particulars including colors, and the specific grid position of features like eyes, nose, mouth. How is pattern recognition the same and different from how humans perceive?
Now, have students consider how these images are very simple (64 pixels) compared to say, a self-driving car recognizing a pedestrian or a cyclist. When asking a computer to perceive photos or even video, the model will need an immense amount of examples to learn from.
ELD Extension: Pose Estimation Person Keep the code and build for the Pose Detect mission open. Have students click on the Camera Icon to view the pose estimation overlaid onto the webcam. Students should back up and stand in front of the camera and watch which body parts map to each dot. Students can also reference the drop down menu from the “camera (nose) pose (X position)” block to see which body parts pose detection works with.
Students should use these resources to draw and label a person with pose detection dots mapped onto each body part, including the list below. Students can draw the person in any pose. (This page has an example image for multiple poses: https://www.tensorflow.org/lite/examples/pose_estimation/overview)
|
|

Students should answer the following questions about their animal search.
ELD Adaptation: COCO Animals
COCO, or Common Objects in Context, is a large-scale object detection, segmentation, and captioning dataset. Students can browse the Coco image dataset at https://cocodataset.org/#explore

Choose 1 animal and click “Search” to view images tagged with that animal.
Students should answer the following questions about their animal search.
 Software Developer: Salary $127,260/yr
Software Developer: Salary $127,260/yr
 Electrical Engineer: Salary $127,260/yr
Electrical Engineer: Salary $127,260/yr
 Data Scientist: Salary $103,500/yr
Data Scientist: Salary $103,500/yr
Circuit A conductive path for the flow of current or electricity.
Power The current or flow of electric charge and voltage.
Microcontroller An integrated circuit containing a microprocessor with memory and associated circuits.
Variables A value that can change depending on conditions or information passed to the program. A storage location with a symbolic name used to keep track of a value that can change while a program is running (similar concept to using X and Y in an algebraic equation). Variables are not only numbers; they can also hold text, including whole sentences (strings) or logical values (true or false).
Input Device A hardware device that sends data to a computer, allowing interaction and control.
Output Device A piece of hardware that converts information into a form humans can sense and understand.
