Learn how to play the Distance Sensor as an instrument.
Piperbot and Pip need help soothing Baby Zomar to sleep. Play your Distance Sensor as an instrument to help. Ask students: “How does your instrument know when and what sound to play? How does an electric keyboard know how to make a sound?”
View student interface at make.playpiper.com Computer with USB port and Chrome or Edge browser
Computer with USB port and Chrome or Edge browser
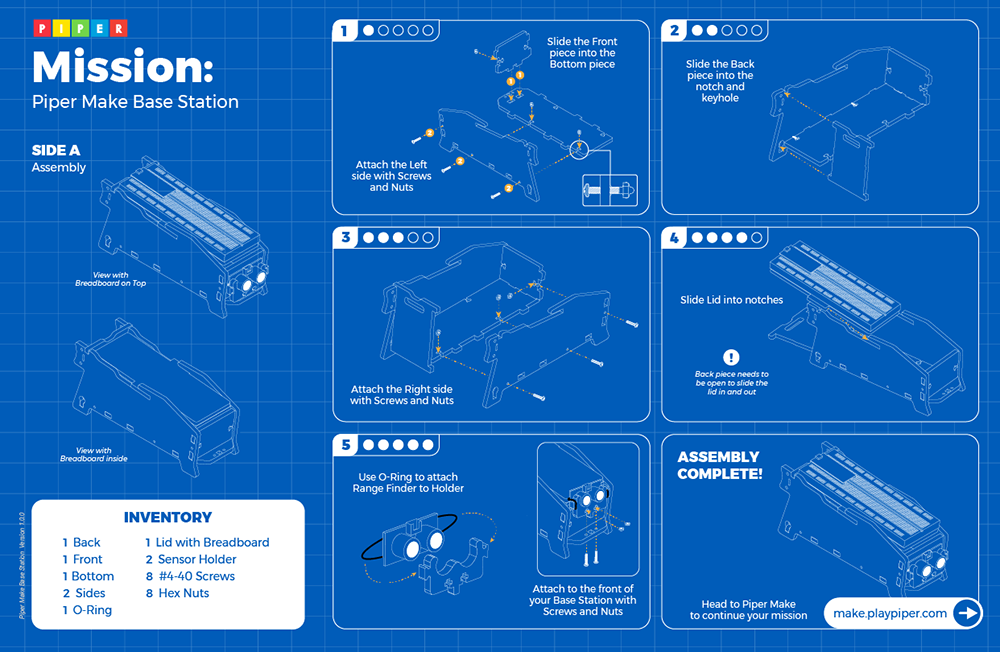
 Piper Make Base Station
Piper Make Base Station
 Robotics Engineer: Salary $104,600/yr
Robotics Engineer: Salary $104,600/yr
 Automotive Engineer: Salary $95,300/yr
Automotive Engineer: Salary $95,300/yr
 Civil Engineer: Salary $88,050/yr
Civil Engineer: Salary $88,050/yr
 Electro-Mechanical and Mechtronics Technicians: Salary $60,570/yr
Electro-Mechanical and Mechtronics Technicians: Salary $60,570/yr
Circuit A conductive path for the flow of current or electricity.
Power The current or flow of electric charge and voltage.
Microcontroller An integrated circuit containing a microprocessor with memory and associated circuits.
Variables A value that can change depending on conditions or information passed to the program. A storage location with a symbolic name used to keep track of a value that can change while a program is running (similar concept to using X and Y in an algebraic equation). Variables are not only numbers; they can also hold text, including whole sentences (strings) or logical values (true or false).
Input Device A hardware device that sends data to a computer, allowing interaction and control.
Output Device A piece of hardware that converts information into a form humans can sense and understand.
